Syndecan-4 Is a Major Syndecan in Primary Human Endothelial Cells In Vitro, Modulated by Inflammatory Stimuli and Involved in Wound Healing - Tram Thu Vuong, Trine M. Reine, Amanda Sudworth, Trond G.

High-resolution Time-lapse Imaging and Automated Analysis of Microtubule Dynamics in Living Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells | Protocol

Investigating Trans-differentiation of Glioblastoma Cells in an In Vitro 3D Model of the Perivascular Niche | ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering

Syndecan-4 Is a Major Syndecan in Primary Human Endothelial Cells In Vitro, Modulated by Inflammatory Stimuli and Involved in Wound Healing - Tram Thu Vuong, Trine M. Reine, Amanda Sudworth, Trond G.

GLUL knockout impairs vessel sprouting a, GLUL mRNA levels in HUVECs... | Download Scientific Diagram

Reconstituting neurovascular unit based on the close relations between neural stem cells and endothelial cells: an effective method to explore neurogenesis and angiogenesis

Physical supports from liver cancer cells are essential for differentiation and remodeling of endothelial cells in a HepG2-HUVEC co-culture model | Scientific Reports

HCMV Infection Reduces Nidogen-1 Expression, Contributing to Impaired Neural Rosette Development in Brain Organoids | Journal of Virology
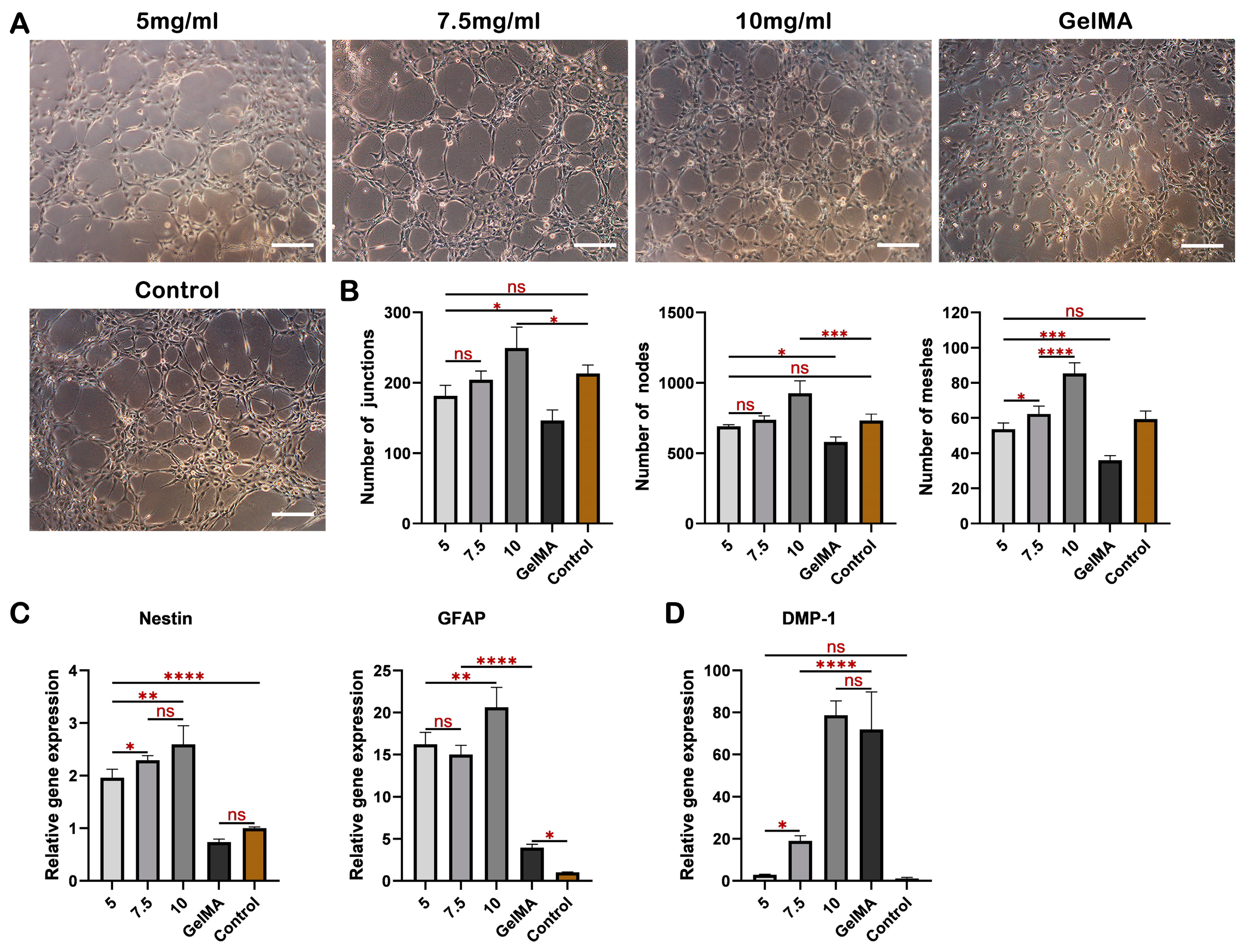
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Injectable Xenogeneic Dental Pulp Decellularized Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel Promotes Functional Dental Pulp Regeneration

Syndecan-4 Is a Major Syndecan in Primary Human Endothelial Cells In Vitro, Modulated by Inflammatory Stimuli and Involved in Wound Healing - Tram Thu Vuong, Trine M. Reine, Amanda Sudworth, Trond G.

Investigating the Interactions of Glioma Stem Cells in the Perivascular Niche at Single‐Cell Resolution using a Microfluidic Tumor Microenvironment Model - Adjei‐Sowah - 2022 - Advanced Science - Wiley Online Library

Physical supports from liver cancer cells are essential for differentiation and remodeling of endothelial cells in a HepG2-HUVEC co-culture model | Scientific Reports

A systems-approach reveals human nestin is an endothelial-enriched, angiogenesis-independent intermediate filament protein | Scientific Reports